Vertical and horizontal
of women is only part of the story. Concentration of women in the
pay
can be explained in part by
of women in part-time
, which are mostly
paid.
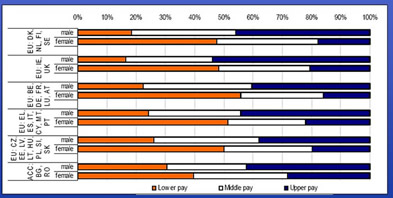
The gender time gap - the
between men and women’s
to the labour market in terms of working time - shows that in the EU27 there is a much higher
of women than men working part time (29% and 7% respectively). Working part time has significant
on pay. Between 70% and 80% of employees working part time
into the low-pay category. However, within the
of part-time workers, the distribution of low pay is quite
between men and women.
When looking at the
in pay between men and women in full-time jobs, a similar
emerges: overall, men tend to be
at the upper end of the income distribution
and there are roughly twice as many women than men among those on low pay.
While more women than men
to work part time, there are
as many men as women working
hours. According to the fourth European Working Conditions Survey, 14.9% of EU27 employees work more than 48 hours a week. When
the gender difference in terms of working long hours, 20% of all
workers work long hours as
to 8.5% of all
employees.